Organic compounds can be classified into different groups to be learnt, which is called homologous series. The features of homologous series are listed as follows:
- having the same functional group
- having the same general formula
- differing from one member to the next by
- a –CH2– unit
- displaying a trend in physical properties
- sharing similar chemical properties due to same functional group
The common homologous series we should understand are:
- alkanes
- alkenes
- alcohols
- carboxylic acids
The following homologous series should understand due to the products from reactions involving series above.
- halogenoalkanes (especially, monohalogenoalkanes)
- esters
2. Formulae
| Formula | Meaning | Example: C5H10 |
| General formula | CnH2n | |
| Empirical formula | the simplest whole number ratio of the different atoms or ions in a compound | CH2 |
| Molecular formula | the number and type of different atoms in one molecule | C5H10 |
| Structural formula | an unambiguous description of the way the atoms in a molecule are arranged | CH2=CHCH2CH2CH3 |
| Displayed formula | to show all the atoms and all the bonds | 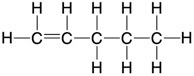 |
3. Other terms
Saturation:
Saturated: all carbon-carbons are single bonds
Unsaturated: one or more carbon-carbon bonds are not single bonds
Hydrocarbons: contain hydrogen and carbon only
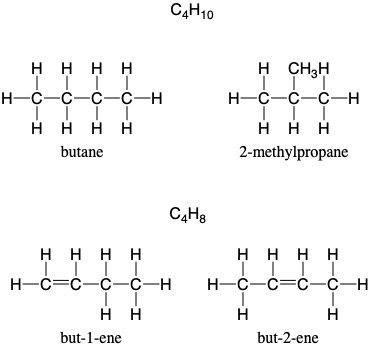
Structural isomers: compounds with the same molecular formula, but different structural formulae.
发表回复