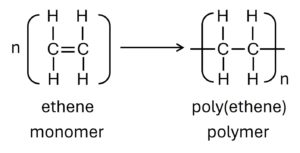
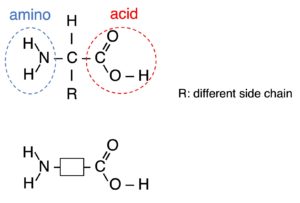
Polymers are large molecules built up from many smaller molecules which called monomers.
3. Summary of different types of polymers
| Addition polymers | Condensation polymers | |
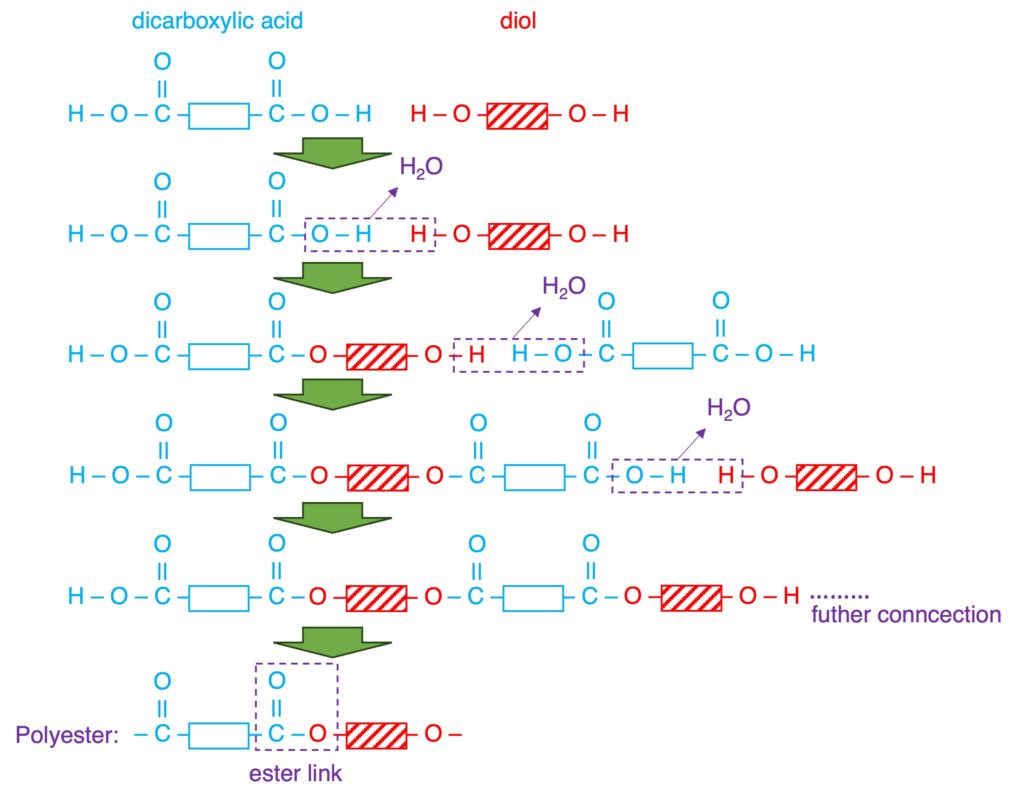
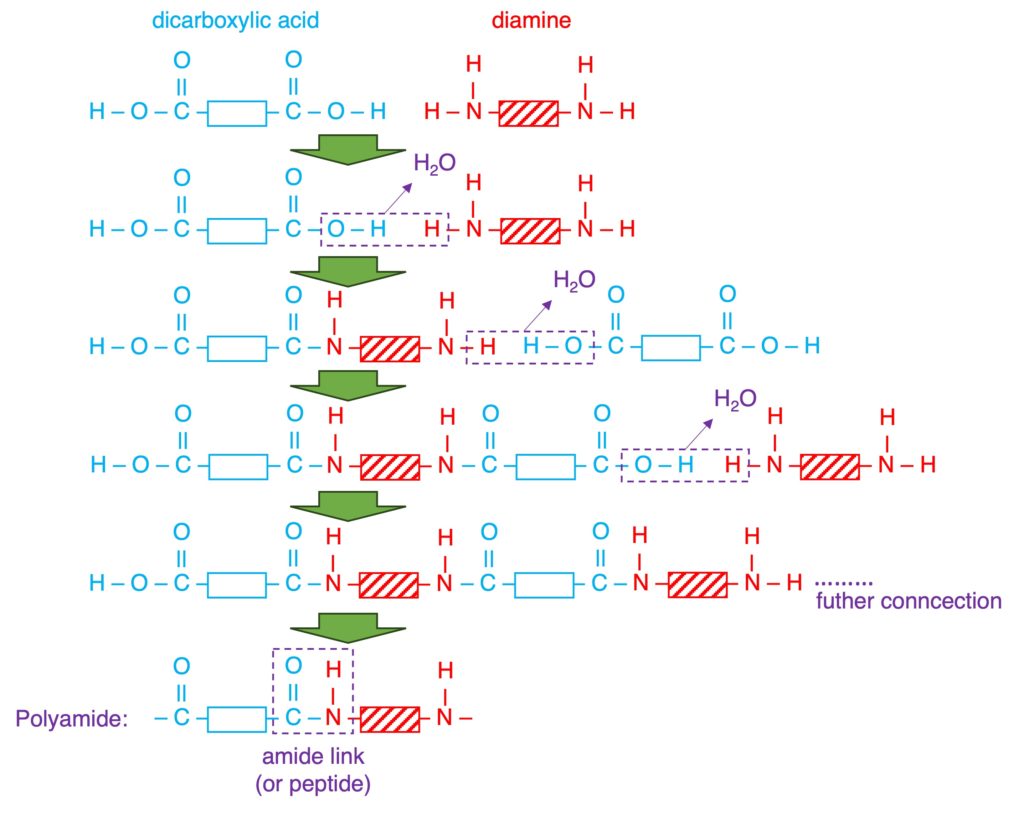
| Reactant (Monomer) | a single monomer “C=C” | two monomers “2 x COOH” and “2 x OH” or “2 x COOH” and “2 x NH2“ |
| Reaction (taking place) | addition opening “C=C” | condensation loss of small molecule (eg: H2O) |
| Products | a single product: polymer non-biodegradable resistant to acids | two products: polymer + small molecule biodegradable (nylon: 40-50 yrs) PET can be hydrolyzed by acids or alkalis. |

发表回复