1. Basic information
- general formula: CnH2n+1COOH (n≥0)
- b.p.: carboxylic acid > alcohol > hydrocarbon
- soluble in water
2. Manufacture of ethanoic acid
By biochemical reaction
by bacteria (Acetobacter)
presence of oxygen (air)
too slow
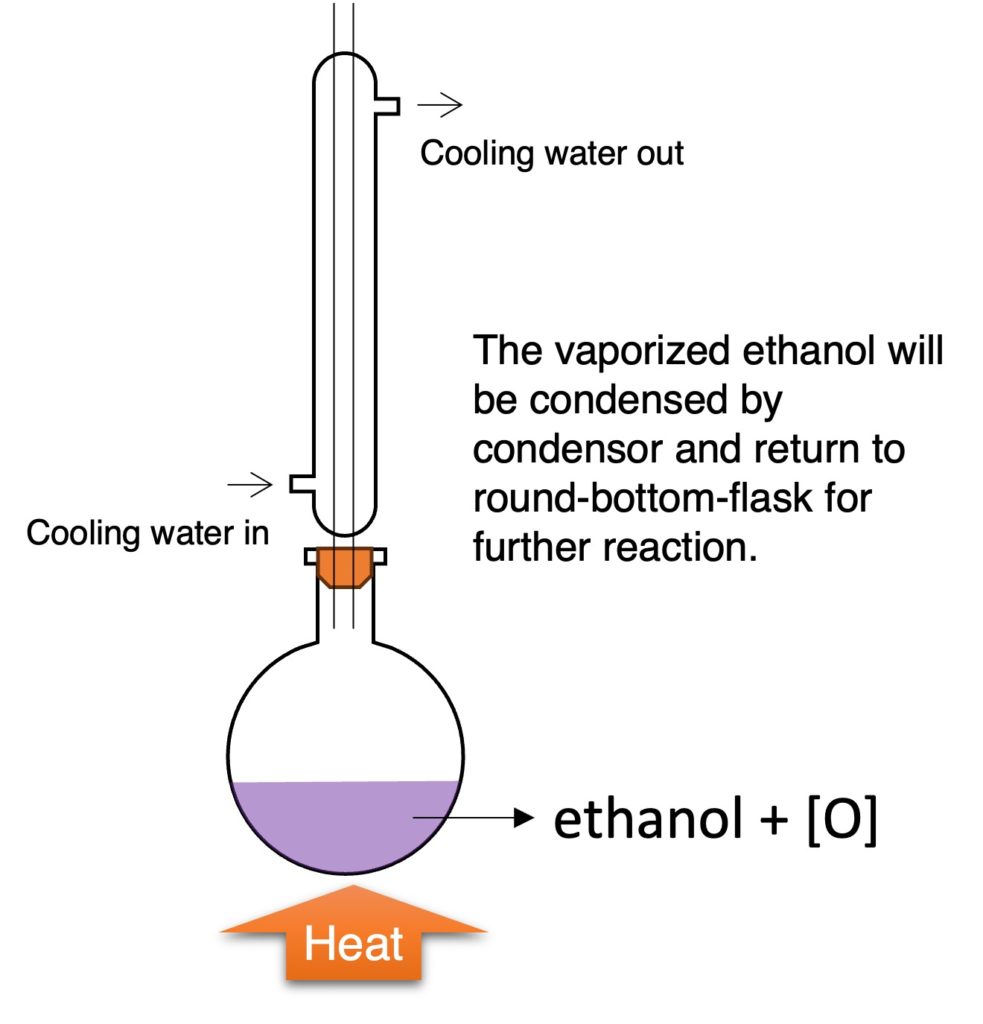
by oxidising agent (symbol: [O])
oxidising agent: acidified potassium manganate (VII), H2SO4 + KMnO4
C2H5OH + [O] → CH3COOH + H2O
Observation: purple (KMnO4) to colorless (if KMnO4 is in limited)
- Carboxylic acids are weak acid. The equilibrium arrow should be used to write the dissociation.
RCOOH ⇌ RCOO– + H+ - neutralisation
CH3COOH + NaOH → CH3COONa + H2O
ethanoic acid + sodium hydroxide → sodium ethanoate + water - react with reactive metal
2CH3COOH + Mg → (CH3COO)2Mg + H2
ethanoic acid + magnesium → magnesium ethanoate + water - react with metal carbonate
CaCO3 + 2CH3COOH → (CH3COO)2Ca + H2O + CO2
calcium carbonate + ethanoic acid → calcium ethanoate + water + carbon dioxide - react with metal oxide
6CH3COOH + Fe2O3 → 2(CH3COO)3Fe + 3H2O
ethanoic acid + iron(III) oxide → iron(III) ethanoate + water
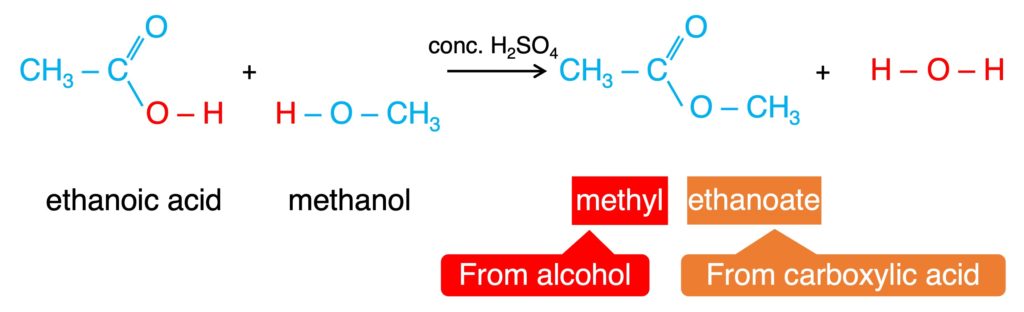
4. Esterificatin: the reaction to produce ester
Carboxylic acid + Alcohol → Ester + Water
This reaction can be catalyzed by H2SO4, and it is a reversible reaction.
Ester is a sweet-smelling oil liquid and can be flavor.
发表回复