1. General information of alcohols
General formula: CnH2n+1OH
Alcohols have higher boiling points than their corresponding alkanes
Alcohols are soluble in water
2. Manufacture of ethanol
Fermentation
C6H12O6 → 2C2H5OH + 2CO2
Conditions:
Catalyst: enzyme (yeast, biochemical catalyst)
Temperature: 25-35 oC
Absence of oxygen
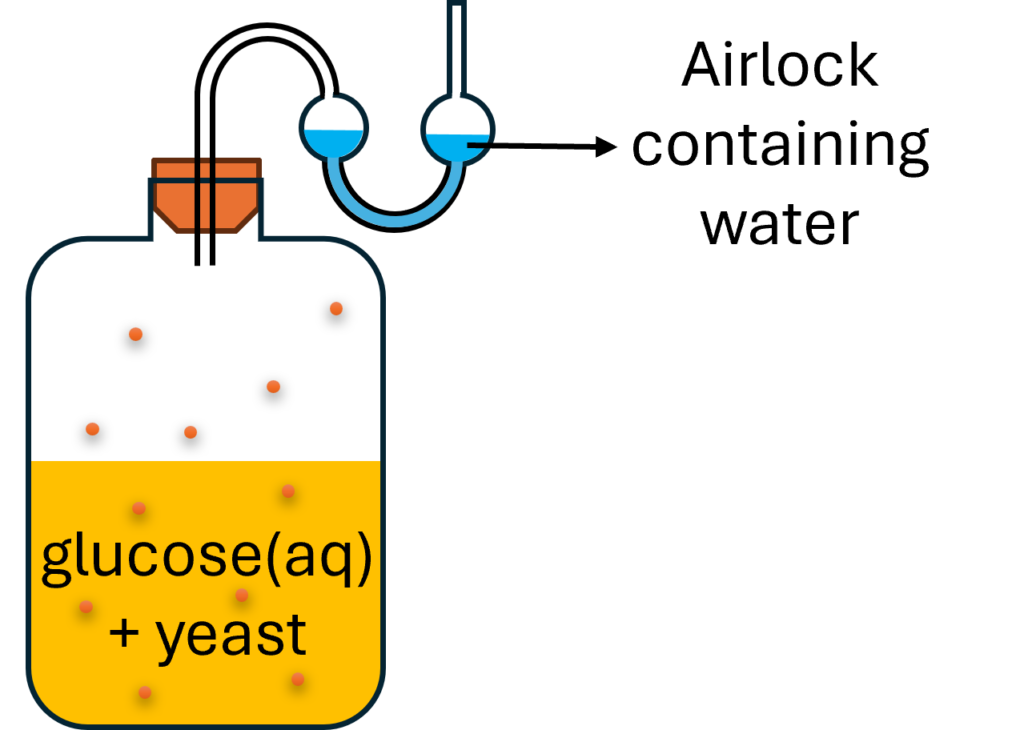
Advantages and disadvantages
- from renewable resource (crop)
- large vessels
- a batch process
- a slow process
- low yield (purified by distillation)
- a simple method
Hydration of ethene
C2H4 + H2O → C2H5OH
Conditions:
Catalyst: H3PO4
Temperature: 300 oC
Pressure: 6000 kPa
Advantages and disadvantages
- from a non-renewable resource (petroleum)
- small-scale equipment capable of withstanding pressure
- a continuous process
- a fast reaction rate
- high yield (pure ethanol)
- a complex method
3. Uses of ethanol
1) Solvent and raw materials for making other organic compounds
2) Fuel
Spirit lamp contains ethanol
Gashol = 10% gasoline + 90% ethanol (alternative transportation fuel)
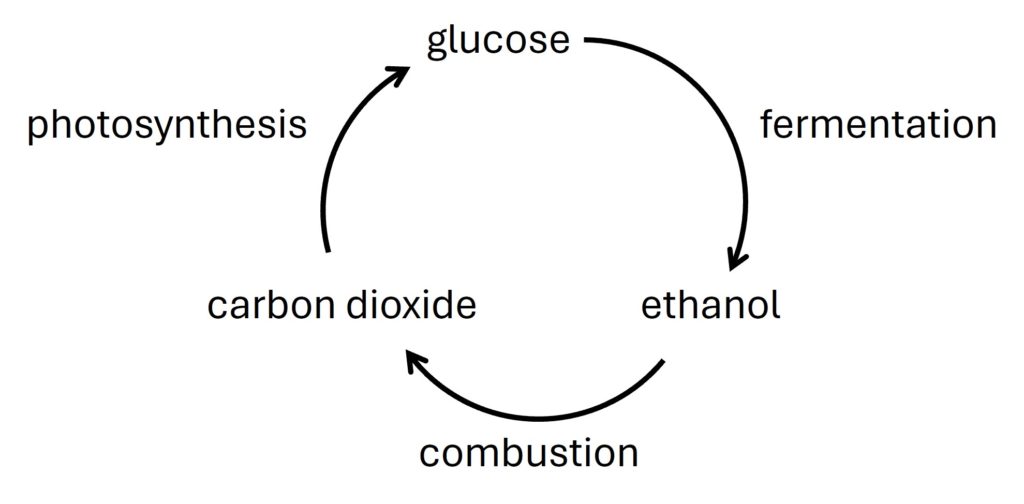
Ethanol which is from fermentation can be considered a green energy.
发表回复