1. Components of air
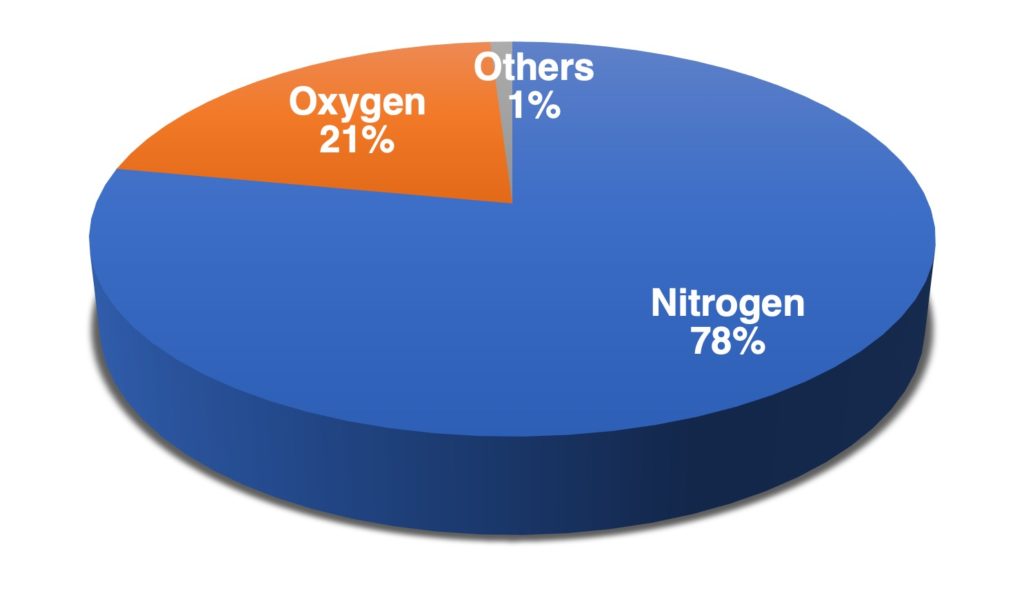
The compositions of clean, dry air as approximately 78% nitrogen, N2, 21% oxygen, O2 and the remainder as a mixture of noble gases and carbon dioxide, CO2.
2. Air pollutants
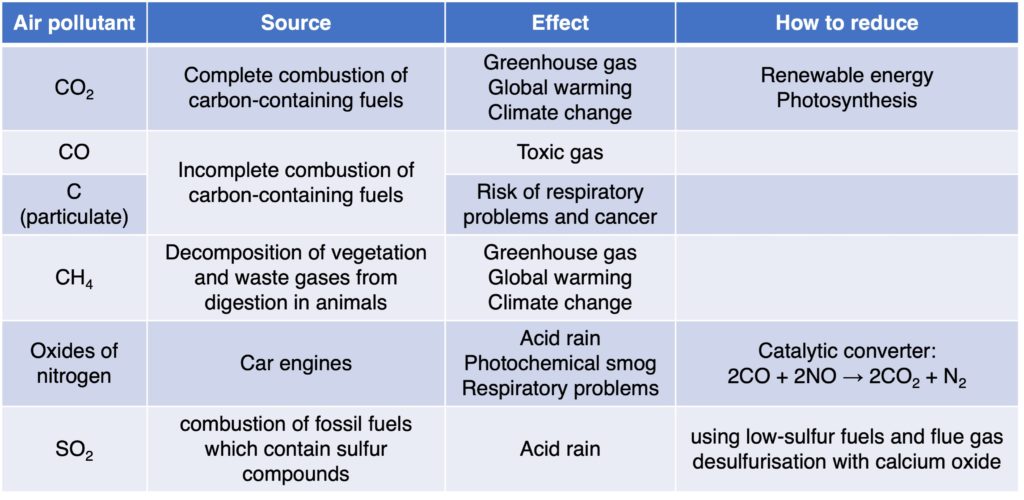
(1) Carbon dioxide, CO2
Carbon dioxide is from the complete combustion of carbon-containing fuels. For example, the complete combustion of octane, C8H18.
2C8H18 + 25O2 → 16CO2 + 18H2O
Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas. A higher level of carbon dioxide leading to increased global warming, which leads to climate change.
(2) Carbon monoxide, CO
Carbon monoxide is from the incomplete combustion of carbon-containing fuels. For example, the incomplete combustion of octane, C8H18.
2C8H18 + 17O2 → 16CO + 18H2O
Carbon monoxide is a toxic gas and can combine with haemoglobin to prevent the carriage of oxygen in blood.
Incomplete combustion can produce carbon particulate (“soot” particles) as well.
2C8H18 + 9O2 → 16C + 18H2O
Particulates will increase risk of respiratory problems and cancer.
(3) Methane, CH4
Some of the reasons for rising levels of methane in the atmosphere are linked to increased cattle farming and more waste being generated by larger populations. Cattle emit large amounts of methane as part of their digestive system. The decomposition of food waste under anaerobic conditions by bacteria at landfill sites also releases large amounts of methane into the atmosphere.
Methane is a greenhouse as well.
(4) Oxides of nitrogen
Oxides of nitrogen (NOx) are from car engines. It includes nitrogen monoxide (NO) and nitrogen dioxide (NO2).They can be produced when nitrogen and oxygen from the air react at high temperatures in engine.
N2(g) + O2(g) → 2NO(g)
2NO(g) + O2(g) → 2NO2(g)
Oxides of nitrogen will produce acid rain.
3NO2(g) + H2O(l) → 2HNO3(aq) + NO(g)
Increasing level of oxides of nitrogen is the formation of photochemical smog. Smog results when several air pollutants react with sunlight to form the characteristic brown haze seen over many large cities.Photochemical smog is harmful to human health, and has been linked to respiratory disease and increased numbers of asthma attacks.
Oxides of nitrogen fin car engines can be removed by catalytic converters:
2CO + 2NO → 2CO2 + N2
(5) Sulfur dioxide, SO2.
Sulfur dioxide is from the combustion of fossil fuels which contain sulfur compounds. When the fuel is burnt, the sulfur combines with oxygen from the air to release sulfur dioxide, SO2.
S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g)
Sulfur dioxide and water vapor in the air to form acid rain. Acid rain is harmful to life both on land and in the water. Increased acidity levels in lakes can kill fish and other aquatic life, while many plants are extremely sensitive to pH levels. Some building materials react with acid rain over time leading to increased rate of damage and corrosion.
Emission of sulfur dioxide can be reduced by using low-sulfur fuels (such as coal wash which means sulfur compounds will be removed before combustion due to their higher density), and flue gas desulfurisation with calcium oxide: SO2 + CaO → CaSO3.
3. Greenhouse gases and greenhouse effect
(1) Greenhouse gases
Carbon dioxide, CO2, and methane, CH4, are two main components of greenhouse gases, which are produced from combustion of fossil fuels and decomposition of vegetation and waste gases from digestion in animals, respectively.
(2) Greenhouse effect
Increasing level of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere will cause global warming which is called greenhouse effect.
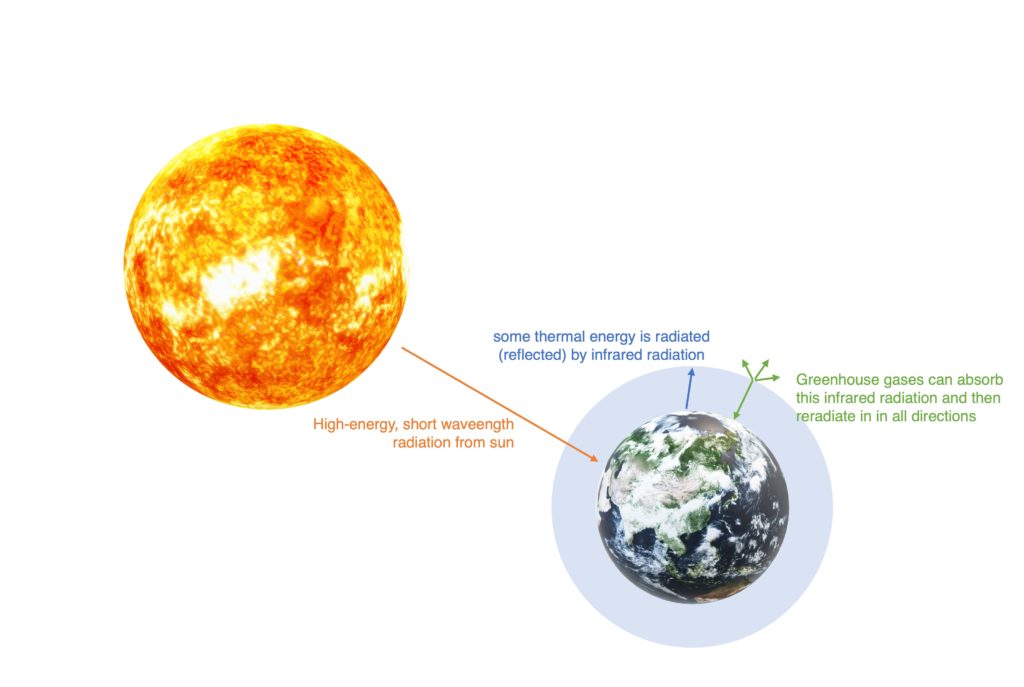
The greenhouse gases allow high-energy, short wavelength radiation from the Sun to pass through the atmosphere and reach the Earth’s surface. Some of this thermal energy is absorbed and heats the oceans and land, and some is radiated (reflected) back into the atmosphere. The heat radiated by the Earth has a lower energy and a longer wavelength. The actual wavelength of this reflected radiation falls within the infrared part of the electromagnetic spectrum. The greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane can absorb this infrared radiation and then reradiate (re-emit) it in all directions. As it is re-emitted in all directions, some does back towards the Earth’s surface. This reduces the heat loss to space and increases the temperature of the lower atmosphere.
(3) Climate change
Photosynthesis as the reaction between carbon dioxide and water to produce glucose and oxygen in the presence of chlorophyll and using energy from light.
carbon dioxide + water → glucose + oxygen
6CO2 + 6H2O → C6H12O6 + 6O2
5. Summary
发表回复