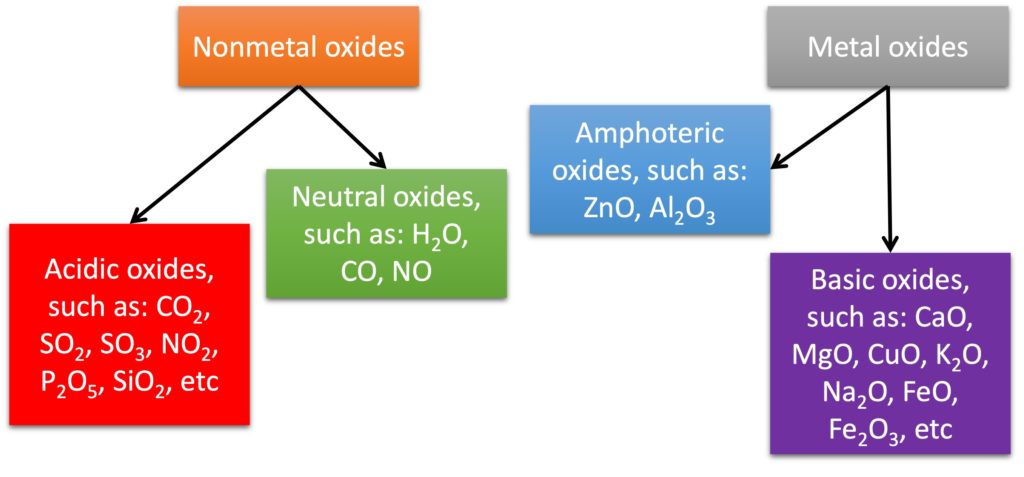
- Acidic oxides
Most nonmetallic oxides are acidic oxides, such as SO2 and CO2.
When these acidic oxides are placed in water, acids will be produced. For instance,
SO2 + H2O → H2SO3 (sulfurous acid)
CO2 + H2O → H2CO3 (carbonic acid)
These oxides can react with base. For example,
CO2 + Ca(OH)2 → CaCO3 + H2O
It does not mean that all nonmetallic oxides can dissolve in water to produce an acidic solution. One example is silicon dioxide (SiO2). It cannot “dissolve” in water to form an acidic solution, but it can react with base, and the chemical equation as shown below:
SiO2 + 2NaOH → Na2SiO3 (sodium silicate) + H2O
2. Basic oxides
3. Neutral oxides
Some nonmetallic oxides cannot “dissolve” in water and react with base, and they are called as neutral oxides, such as CO (carbon monoxide), NO (nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide) and N2O (nitrogen(I) oxide, dinitrogen monoxide).
The meaning of term “amphoteric” is “both”. It means these oxides can react both acids and bases, such as Al2O3 and ZnO.
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
Al2O3 + 2NaOH → 2NaAlO2 (sodium aluminate) + H2O
ZnO + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2O
ZnO + 2NaOH → Na2ZnO2 (sodium zincate) + H2O
发表回复