4.1 Electrolysis
1. What is electrolysis?
Electrolysis is a decomposition of an ionic compound when molten or in aqueous solution, by the passage of an electric current.
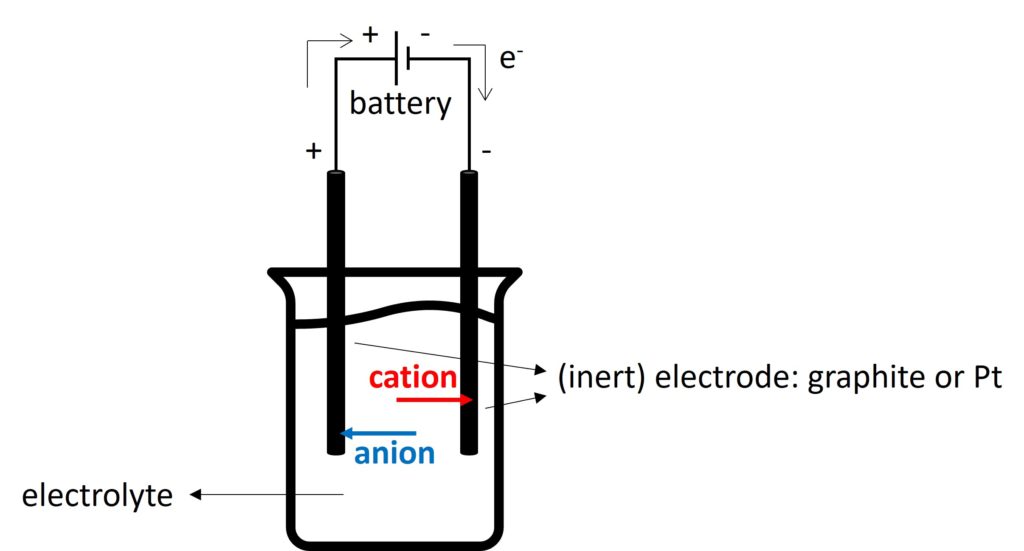
The common apparatus of electrolysis is shown below.
Electrodes used here are called inert electrode, which means they cannot react during electrolysis. The only purpose of inert electrodes is to conduct electricity because of delocalized electrons.
Electrolyte is an ionic compound when it is molten or in aqueous solution, which can conduct electricity by free-moving ions.
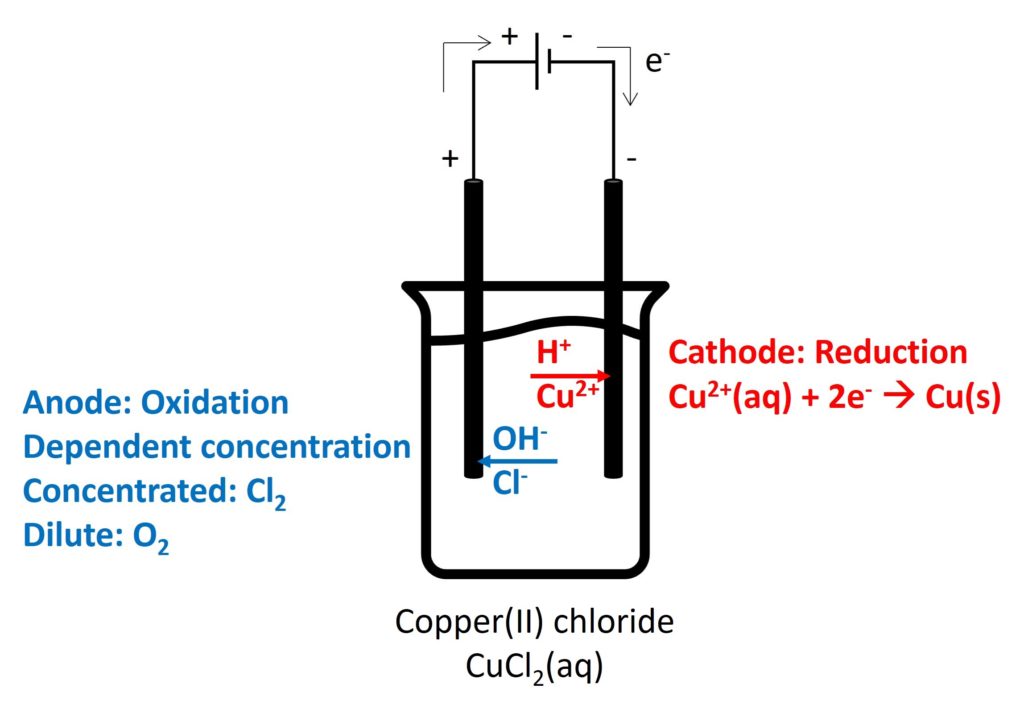
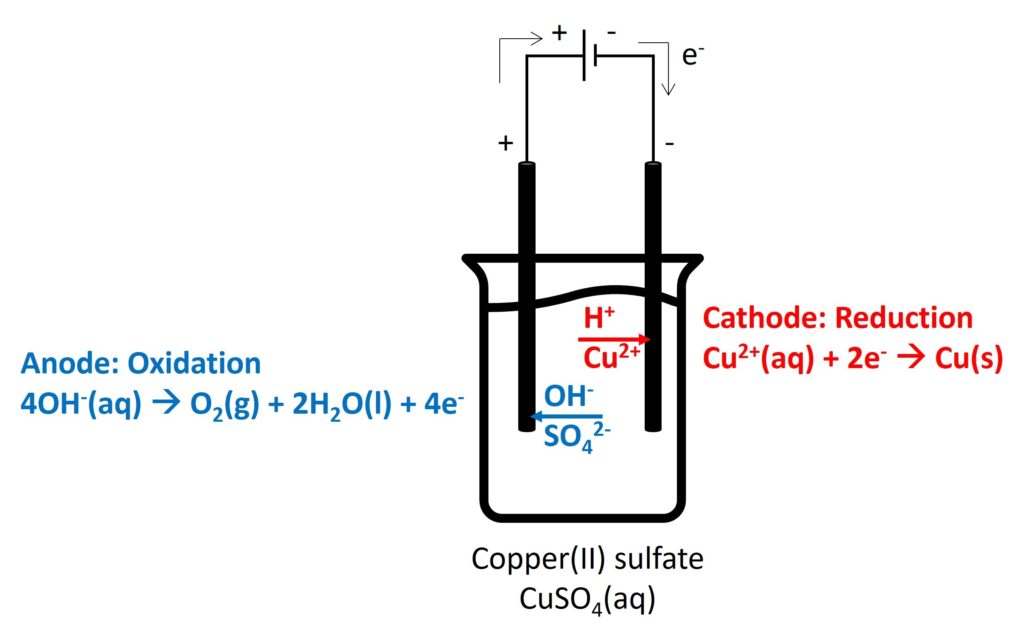
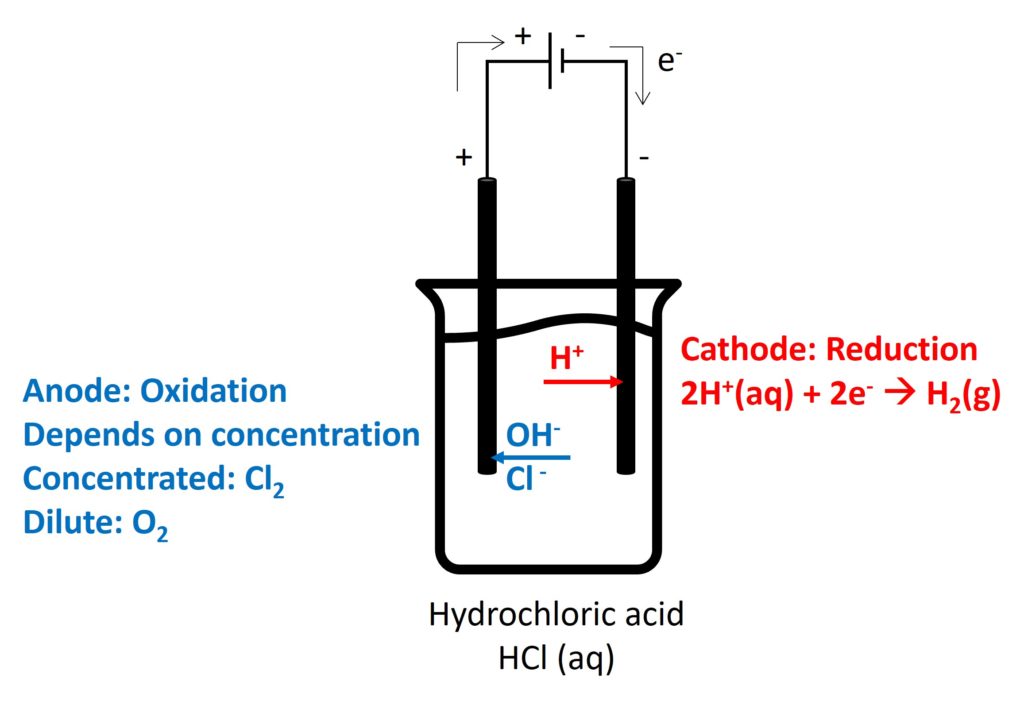
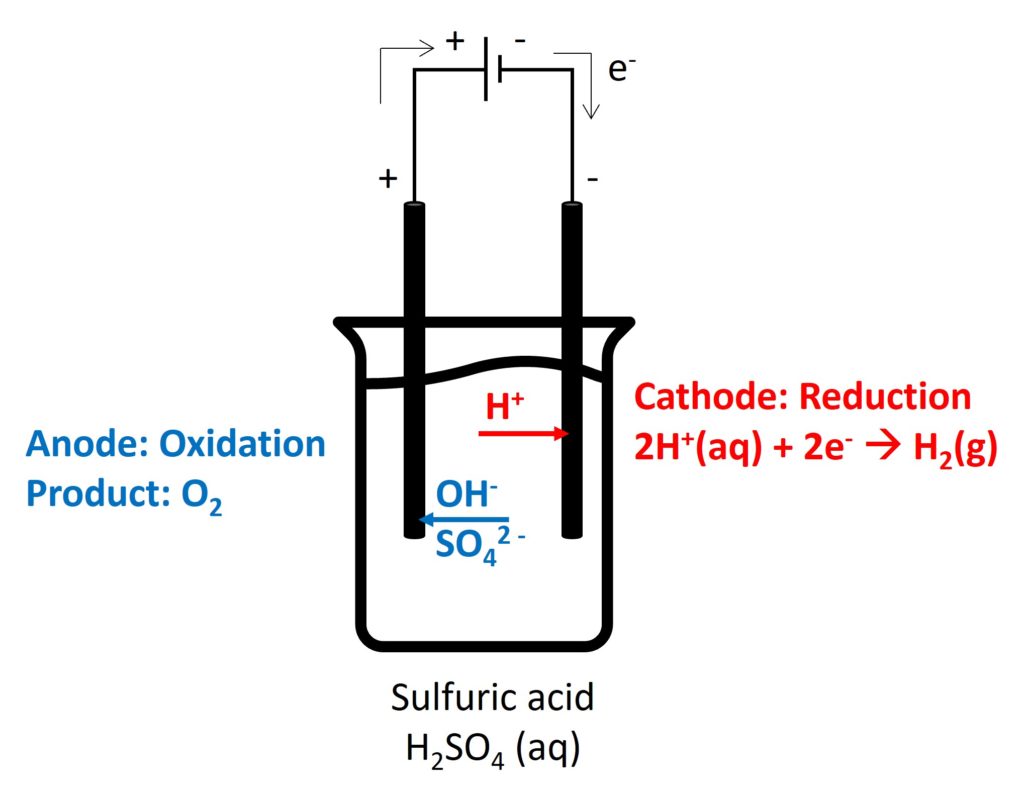
Cation will move to negative electrode to be reduced and anion will move to positive electrode to be oxidised.
The electrode which occurs oxidation is called anode and the electrode which occurs reduction is called cathode.
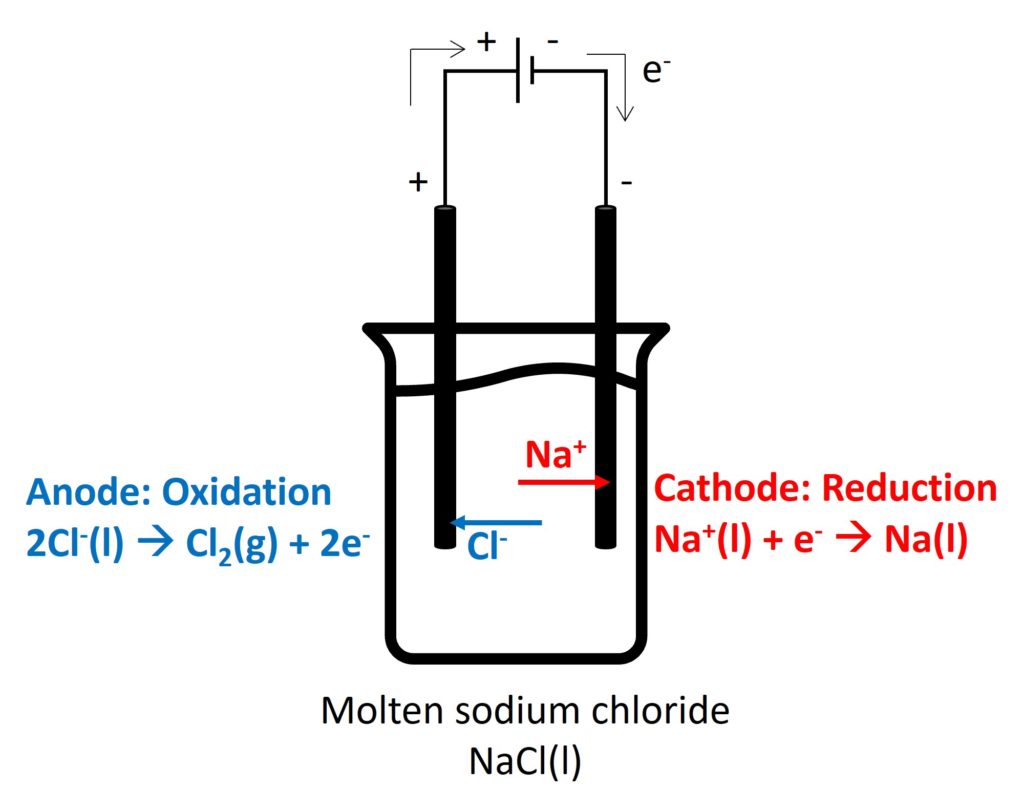
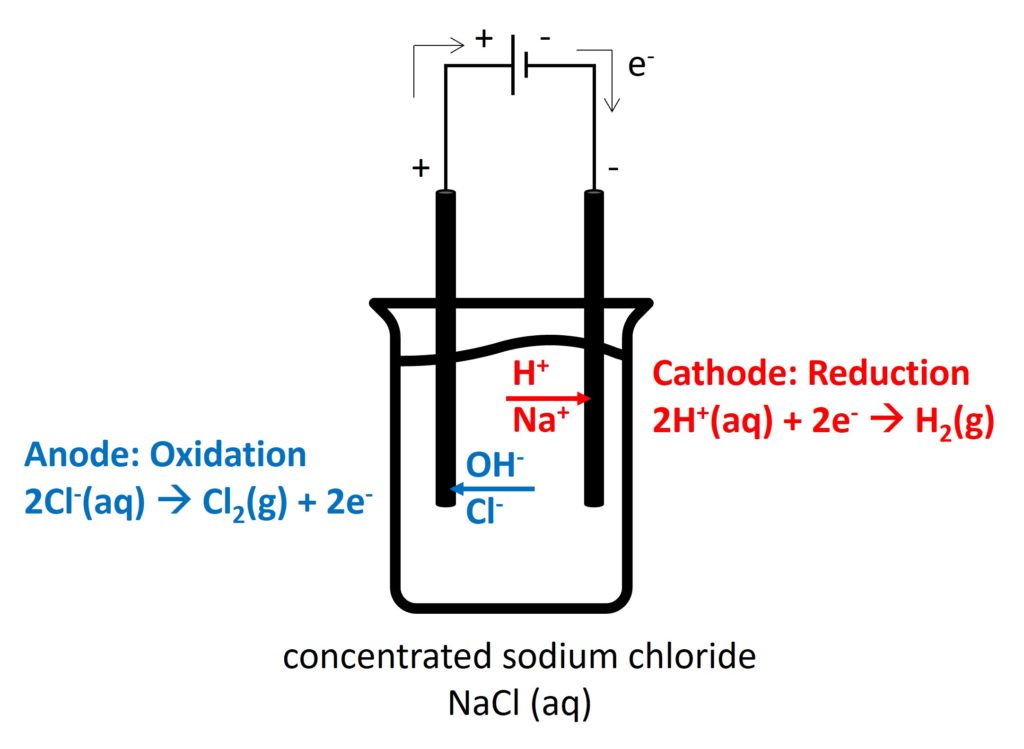
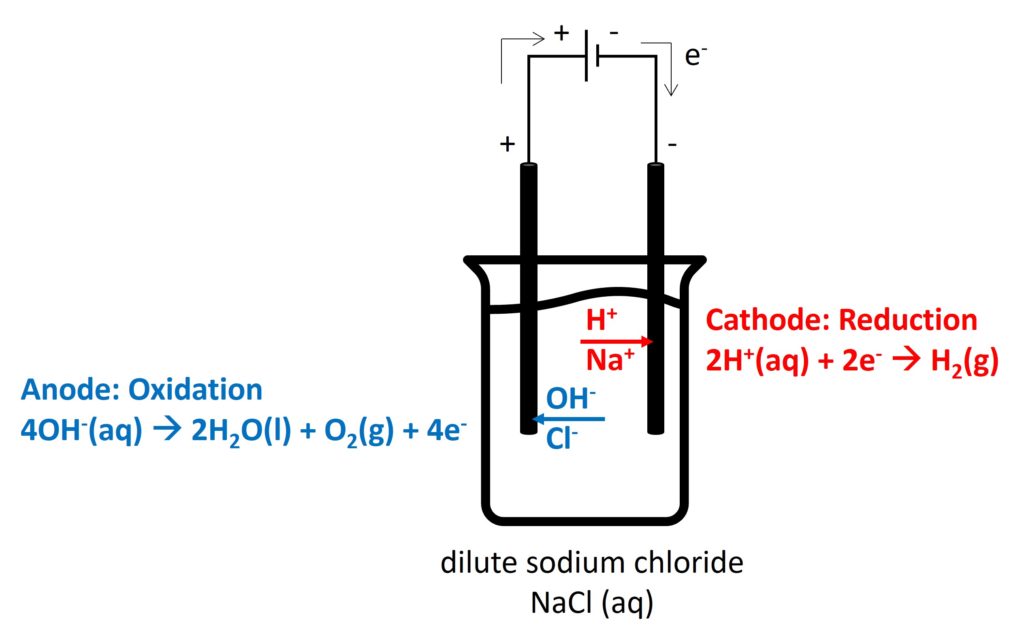
2. Electrolysis in different electrolytes
Gaseous products (such as, O2, Cl2, and H2): bubbles appeared
How to test these gases:
Cl2: decolorize damp litmus paper
O2: relight
H2: pop sound
Colour of electrolyte:
CuSO4(aq): blue
the colour intensity depends on the concentration of Cu2+. If concentration of Cu2+ unchanged, the colour intensity remains constant.
3. Electrolysis by copper electrode (purification)
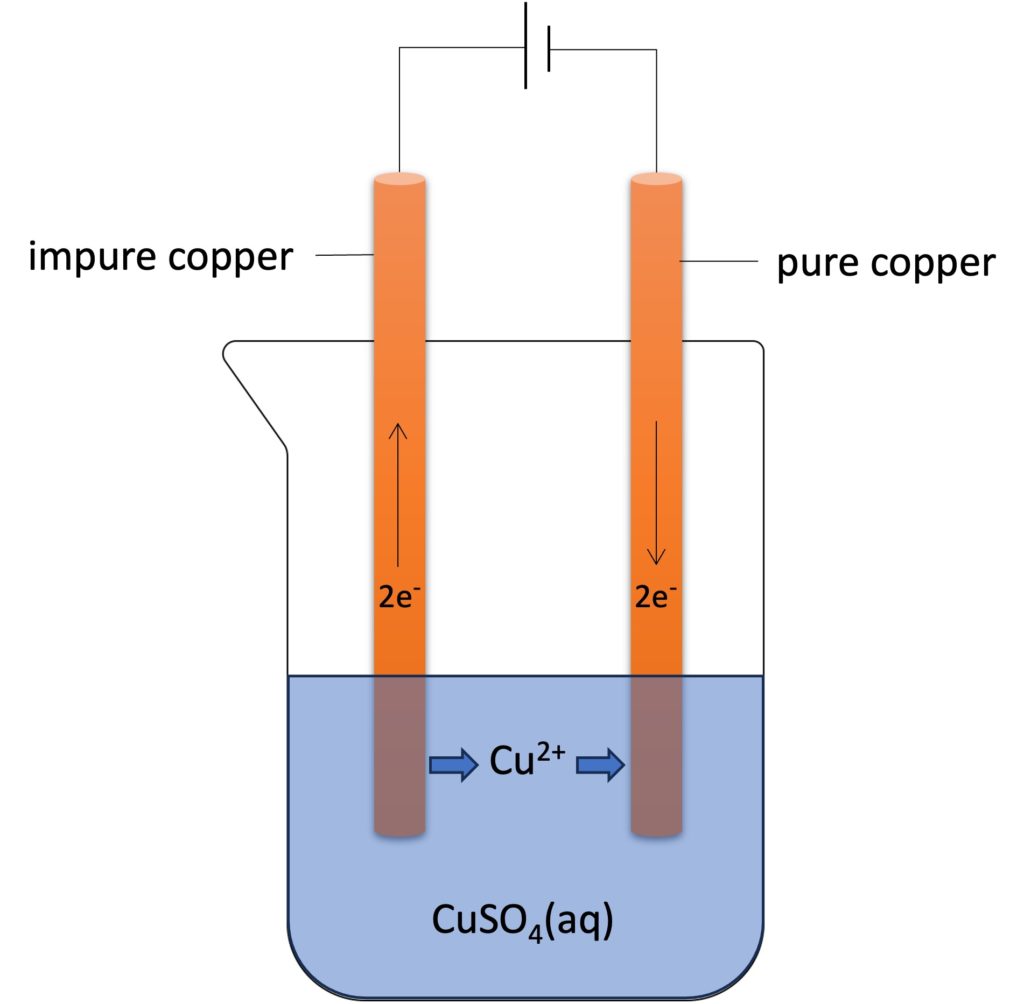 Copper can be purified by electrolysis. For this propose, two copper electrodes will be used. An impure copper electrode connects to positive terminal, and pure copper electrode connects to negative terminal. In this case, copper electrodes will participate electrolysis, and copper will be transferred from positive electrode (anode) to negative electrode (cathode).
Copper can be purified by electrolysis. For this propose, two copper electrodes will be used. An impure copper electrode connects to positive terminal, and pure copper electrode connects to negative terminal. In this case, copper electrodes will participate electrolysis, and copper will be transferred from positive electrode (anode) to negative electrode (cathode).
During purification, the concentration of electrolyte remain constant, so that the color intensity of copper(II) sulfate solution remain constant.
4. Electroplate
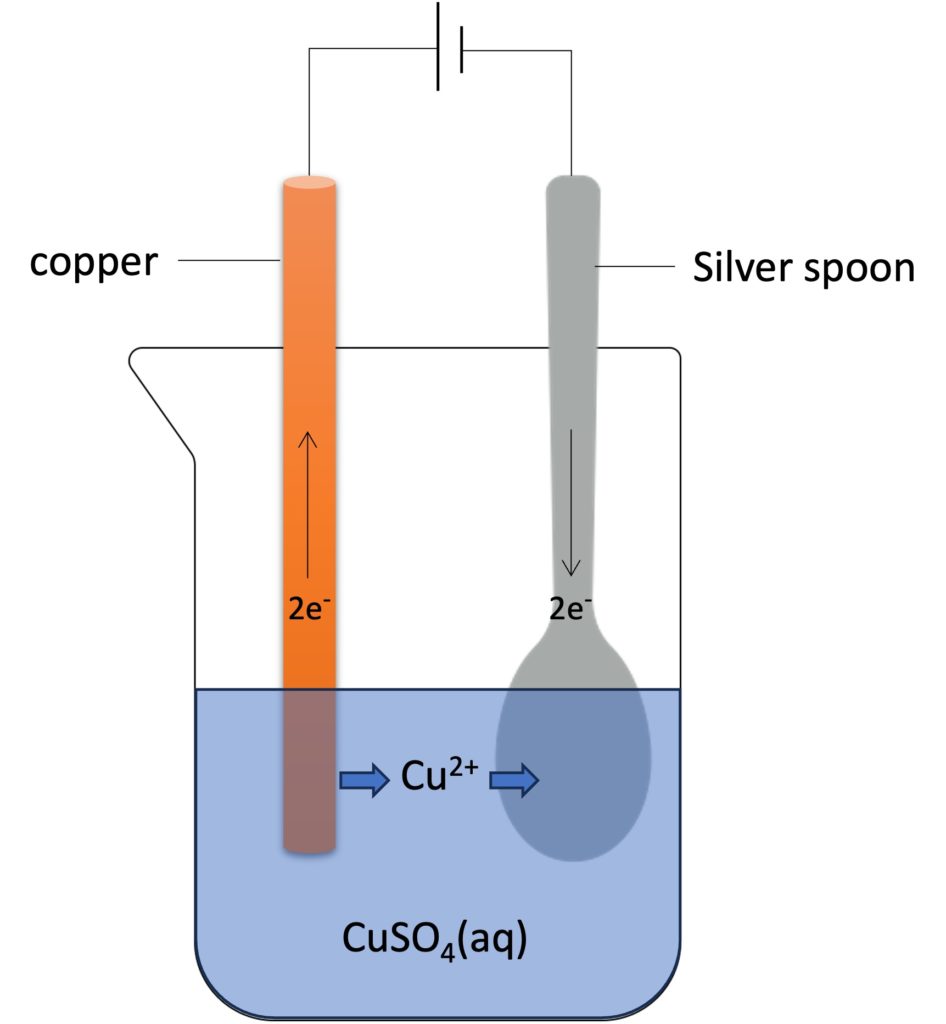 Electroplate (figure above) is another application of electrolysis. The purpose of electroplate is to make an object which covers by another metal. In this case, a silver spoon was placed in a copper(II) sulfate solution. The red-brown copper can be covered on the silver spoon on cathode (negative electrode).
Electroplate (figure above) is another application of electrolysis. The purpose of electroplate is to make an object which covers by another metal. In this case, a silver spoon was placed in a copper(II) sulfate solution. The red-brown copper can be covered on the silver spoon on cathode (negative electrode).
The purpose of electroplate can be a) performance and b) anti-corrosion etc.