6.3 Reversible reactions and equilibrium
1. Features of equilibrium
When the reversible reaction achieves the state of equilibrium in a closed system,
a) the rate of the forward reaction is equal to the rate of the reverse reaction;
b) the concentrations of reactants and products are no longer changing.
3. Factors affect the position of equilibrium
Addition of CH3COOH or C2H5OH. Equilibrium will shift to right side to consume the additional reactants.
Removal of water. Equilibrium will shift to right side to replace the loss of water.
Increasing pressure favours to the side which has less gaseous particles.
Decreasing pressure favours to the side which has more gaseous particles.
Exercises: State and explain how increasing pressure affects the yield in the following reaction.
a) 2NO(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2NO2(g)
Increase. Less gaseous particles in the right side.
b) H2(g) + Cl2(g) ⇌ 2HCl(g)
No effect. Same amount of gaseous particles on both side.
Increasing temperature favours to endothermic process.
Decreasing temperature favours to exothermic process.
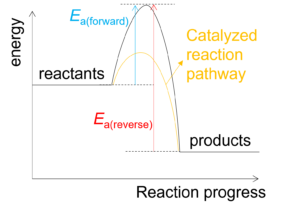
Catalyst cannot affect the position of equilibrium because catalyst can speed up both forward and reverse reactions equally by lowering activation energy for both forward and reverse reactions (see the following diagram).
A(g) + 2B(g) ⇌ AB2(g) ΔH<0
| Change in | Position of equilibrium | Explain | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concentration | Add some A | shifts to right side | to consume the additional A |
| Remove some B | shifts to left side | to replace the loss of B | |
| Pressure | compress volume to increase pressure | shifts to right side | less gaseous particles in the right side |
| decrease pressure | shifts to left side | more gaseous particles in left side | |
| Temperature | increase temperature | shifts to left side | reverse reaction is endothermic |
| decrease temperature | shifts to right side | forward reaction is exothermic | |
| catalyst | addition of catalyst | no effect | catalyst speeds up both forward and reverse reactions equally |